Basic Fact Pattern
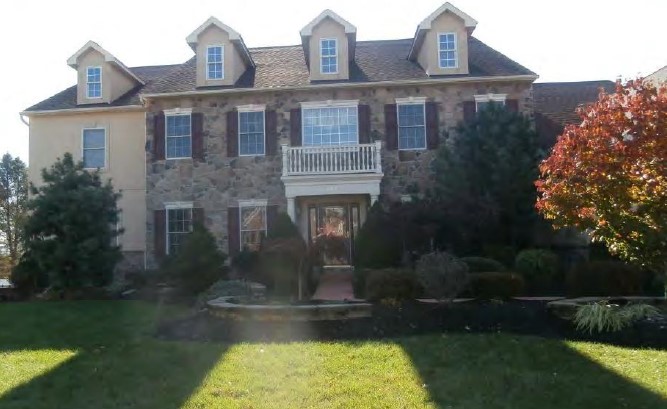
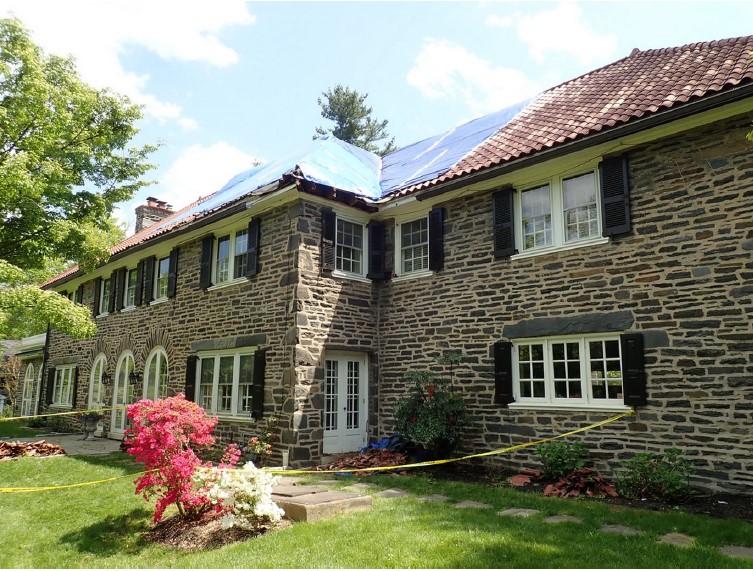
- Development of 250 units, including a clubhouse building, townhomes, and single family residences.
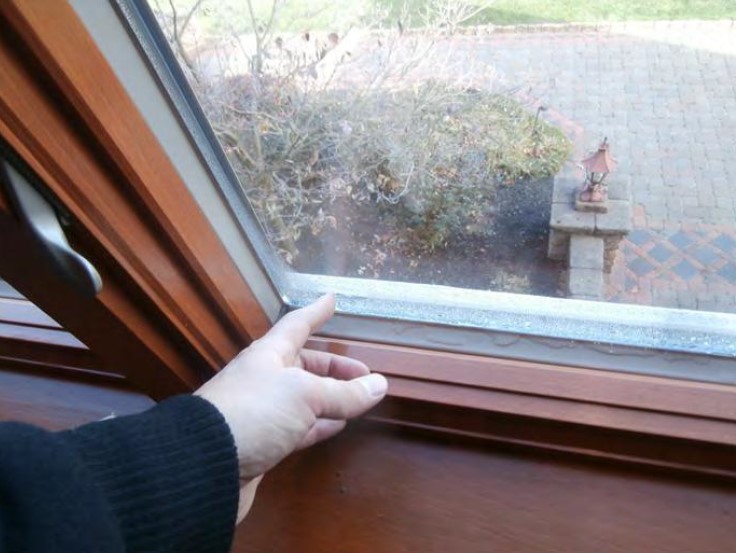
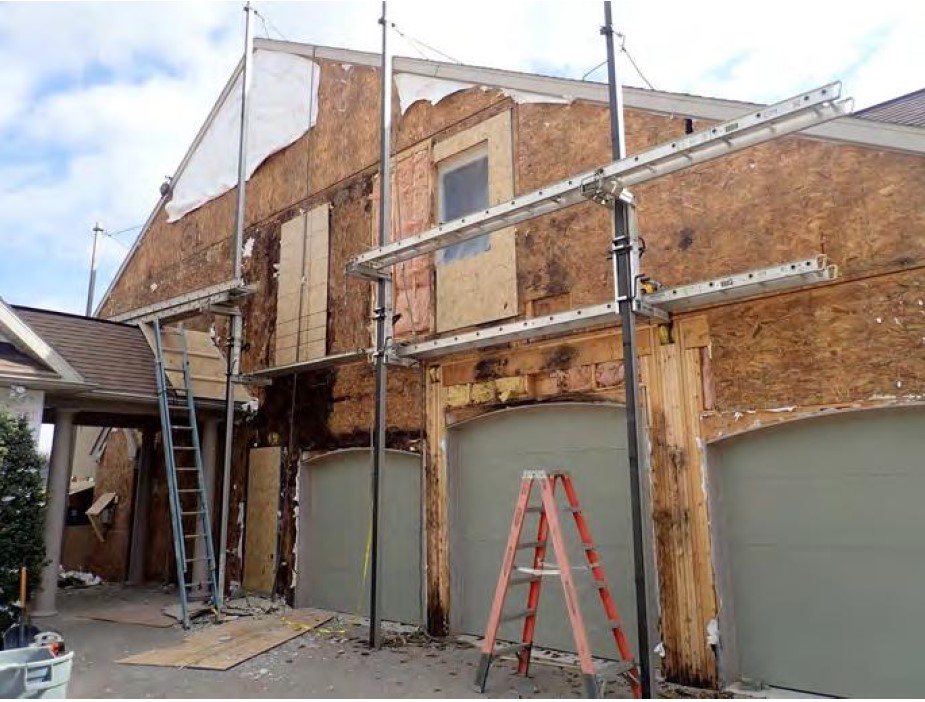
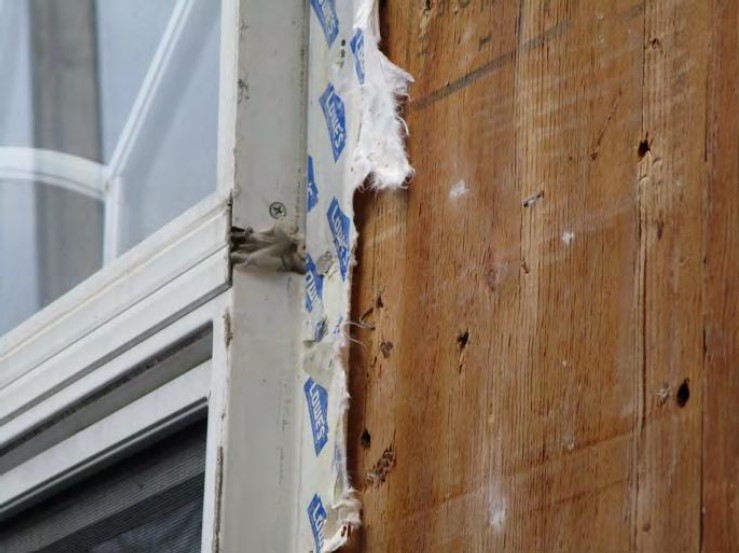
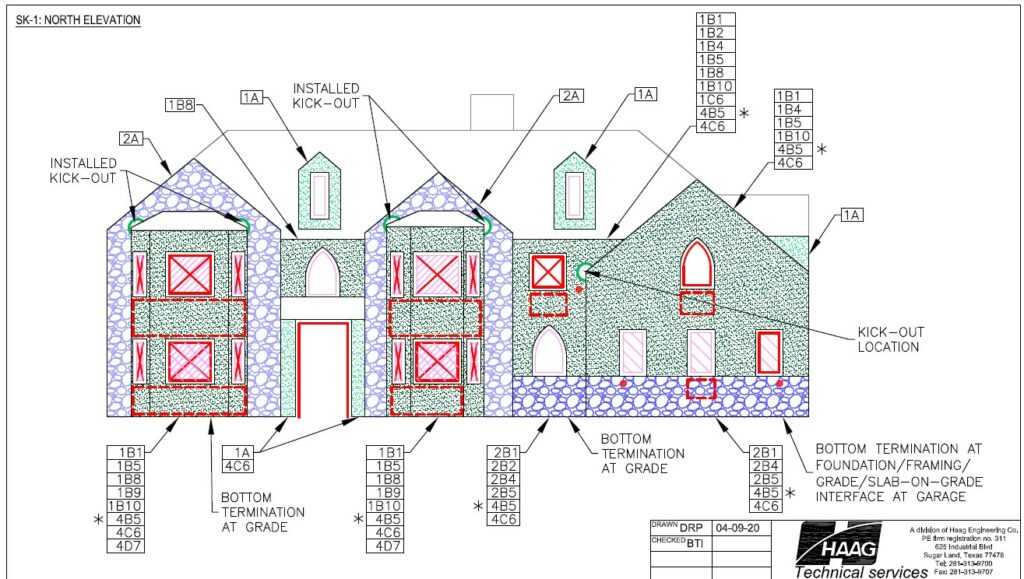
- Alleged construction defects in the exterior claddings resulting in systemic moisture intrusion and underlying structural damage.
- Exterior claddings consisted of combinations of vinyl siding, hardcoat stucco, and adhered stone veneer.
- Alleged damages included complete re-cladding of all buildings.


Investigative Sciences Employed
- All 250 buildings were visually inspected.
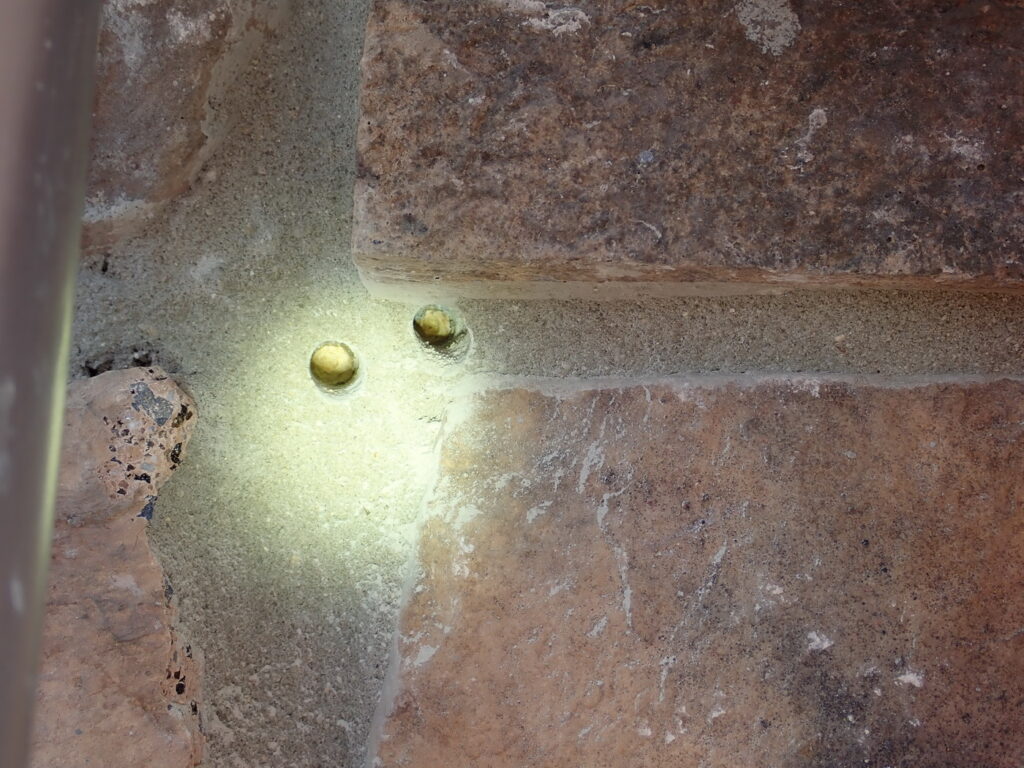
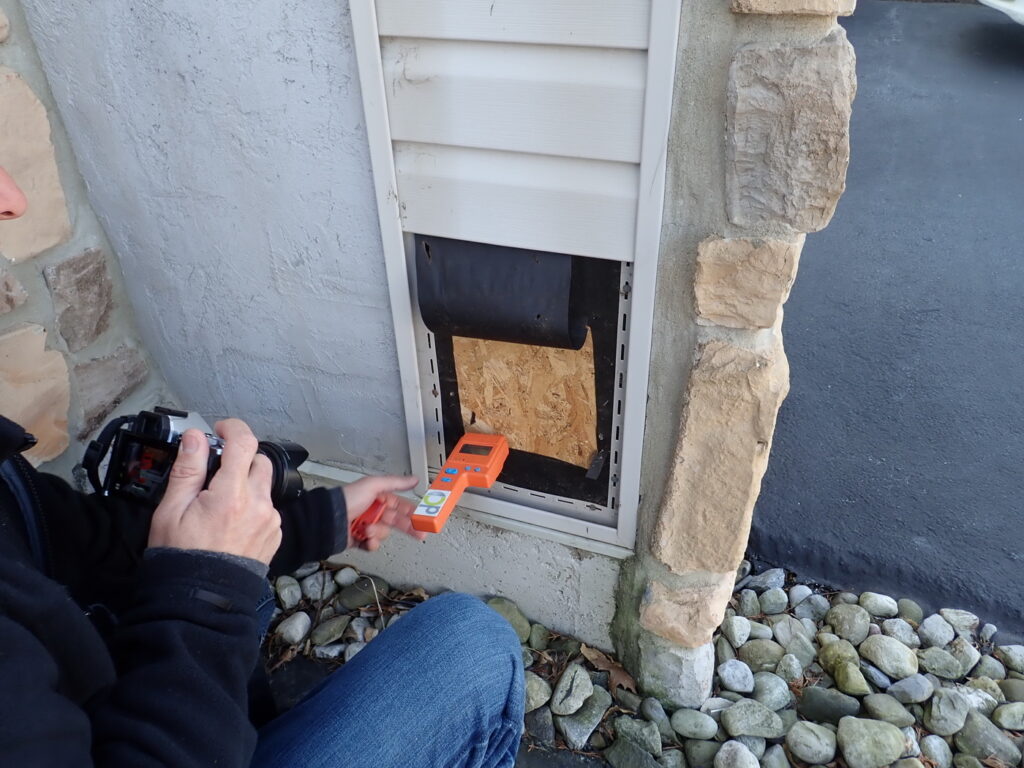
- Moisture probe tests were performed on a representative sampling of buildings of each type.
- Destructive test cuts were performed and a separate representative sampling of buildings of each type.
- Detailed analyses of opposing expert investigational methods were performed.
- Comprehensive code analysis was performed across the three building codes represented across the timeframe of construction for the differing phases of the development.


Determinations Made
- Actual moisture intrusion was minimal, localized, isolated, and associated with discrete, non-systemic causes.
- Complete exterior re-cladding was not required.
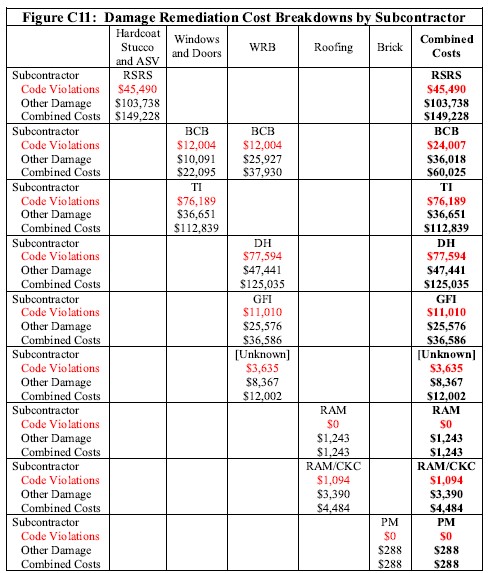
- A remedial action plan was developed, along with a cost to perform the repairs.
- Litigation support services were also provided throughout alternative dispute resolution.
Involved Experts: